Plastic pollution is a major sustainable development challenge. Single-use plastic packaging accounts for nearly half of the global annual plastic waste, and most of it is not biodegradable. 91% of plastic waste is either landfilled or incinerated, forming microplastics that harm human health and marine life. Existing bioplastics have shortcomings: polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) has poor mechanical properties, and polylactic acid (PLA) lacks biodegradability at room temperature and is difficult to achieve multifunctionality simultaneously.

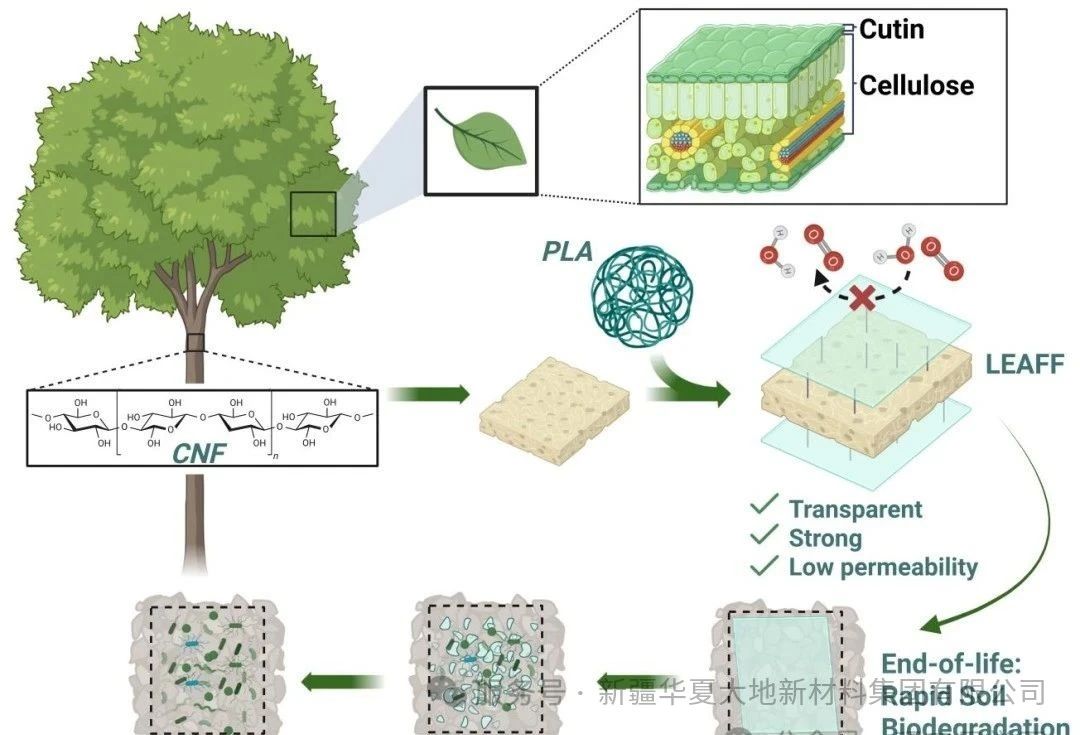
A team led by Professor Joshua S. Yuan from Washington University in St. Louis, USA, and Professor Susie Y. Dai from Texas A&M University, among others, inspired by the structure of plant leaves, have developed a biomimetic layered, ecological, advanced, and multi-functional film (LEAFF). This film is based on cellulose nanofibers (CNF) and coated with PLA, which is cross-linked with hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) to enhance mechanical strength. It enables PLA to be completely biodegradable in environmental soil within five weeks, and also features high transparency, water stability, and high gas tightness. The related work was published in Nature Communications under the title "Biomimetic layered, ecological, advanced, multi-functional film for sustainable packaging".
LEAFF (Layered, Ecological, Advanced, multi-Functional Film) is a biomimetic multi-functional film inspired by the structure of plant leaves. It is composed of a cellulose nanofiber (CNF) core, a poly(lactic acid) (PLA) coating, and a hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) crosslinking agent. It overcomes the existing limitation of bioplastics that high strength and degradability cannot be achieved simultaneously. Its tensile strength reaches 118.1 ± 8.6 MPa (exceeding traditional petroleum-based plastics), and it can completely degrade in normal temperature soil within 5 weeks. It also features high transparency, good water stability, and gas barrier properties (oxygen permeability of 0.772 cm³·m⁻²·day⁻¹·atm⁻¹), meeting the requirements of sustainable packaging and providing a new solution for replacing petroleum-based plastics. However, it still faces challenges in large-scale production and cost control.