Boasting excellent performance and prominent metal substitution potential, new materials are widely applied in automotive, electronics, daily life and other fields, bringing significant opportunities to industries. China's supply capacity of new materials has improved, with remarkable achievements in import substitution of some products. As an important direction for the transformation and upgrading of China's manufacturing industry, this sector has made substantial progress in recent years.

The Following Are Some New Materials That Have Achieved Breakthroughs in Domestic Substitution
I. Nylon 66: Significant Room for Domestic Substitution of Mid-to-high-end Products
Overview of the Nylon 66 Industry
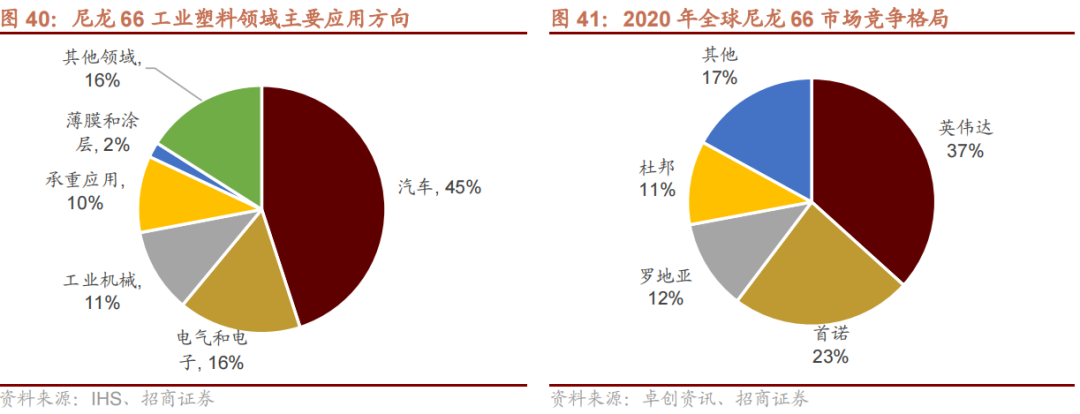
Domestic Substitution Status of Nylon 66
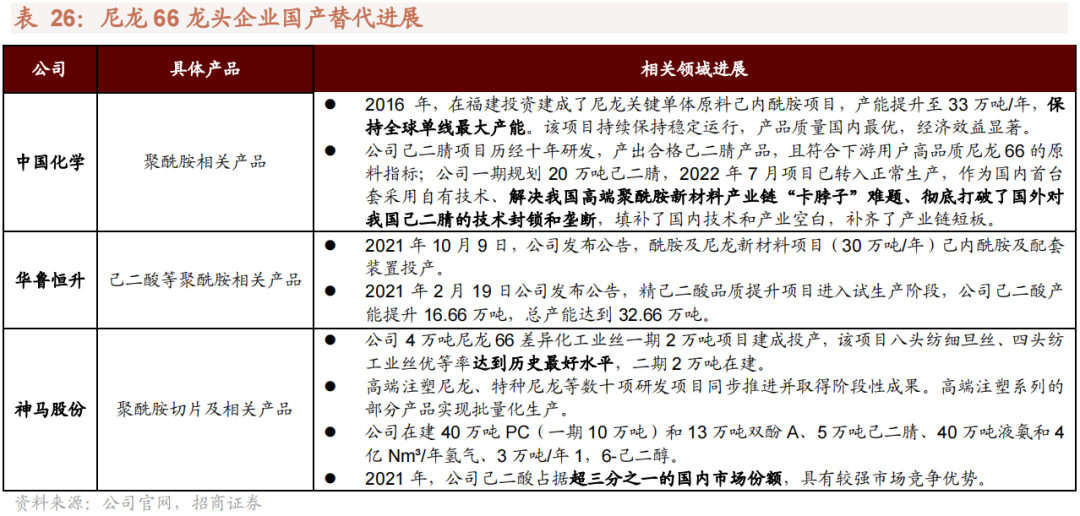
- Huafon Group: It adopted the adipic acid process, constructed an adiponitrile production capacity of 300,000 tons, and realized self-supply.
- Tianchen Qixiang (a subsidiary of China National Chemical Engineering Co., Ltd.): It developed the "direct hydrocyanation of butadiene process", built an adiponitrile production capacity of 200,000 tons, and filled the domestic gap.
- Shenma Co., Ltd.: It explored a process that bypasses adiponitrile, directly producing aminocapronitrile via ammoniation and dehydration of caprolactam, followed by hydrogenation to obtain hexamethylenediamine, thereby reducing reliance on imported raw materials.
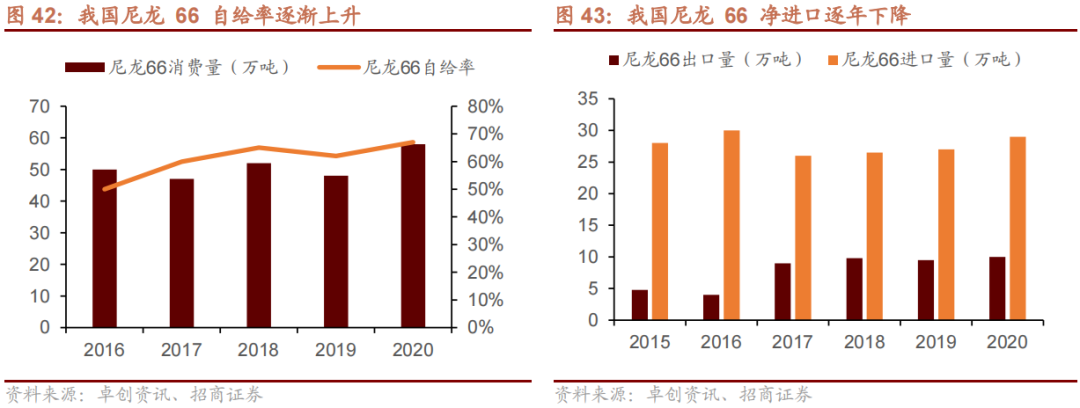
With the continuous domestic localization of adiponitrile raw materials, domestic enterprises have actively deployed the nylon 66 chip industrial chain, and the situation of external dependence on chips is expected to be significantly alleviated. Currently, China has strong import demand for nylon 66 chips. As domestic PA66 production capacity increases, imports have dropped sharply. From January to May 2025, PA66 imports decreased by 33.56% year-on-year, while exports increased by 6.54% year-on-year, and domestic products have achieved substantial substitution in the mid-to-low-end market. The nylon 66 industrial chain is expected to witness rapid expansion along with the localization of raw materials, driving the overall price center of the industrial chain downward through new supply and boosting the rapid growth of downstream demand.
II. Polylactic Acid (PLA): Domestic Market in Short Supply with Broad Application Prospects
PLA Industry Overview
Polylactic acid (PLA), also known as polylactide, is a polyester polymer synthesized using lactic acid as the primary feedstock. It is a novel biodegradable material and ranks among the earliest applications of synthetic biology in the materials sector.
The lactic acid or lactide required for PLA production can be derived from renewable resources through fermentation, dehydration, and purification processes. The resultant PLA typically boasts excellent mechanical and processing properties. Moreover, PLA products can be rapidly degraded via various approaches after disposal, offering exceptional environmental value. For these reasons, PLA has emerged as the most vigorously developed and fastest-advancing biodegradable plastic in recent years.
Polylactic acid (PLA) is an eco-friendly bio-based biodegradable material with broad application prospects, and its global production capacity keeps rising.
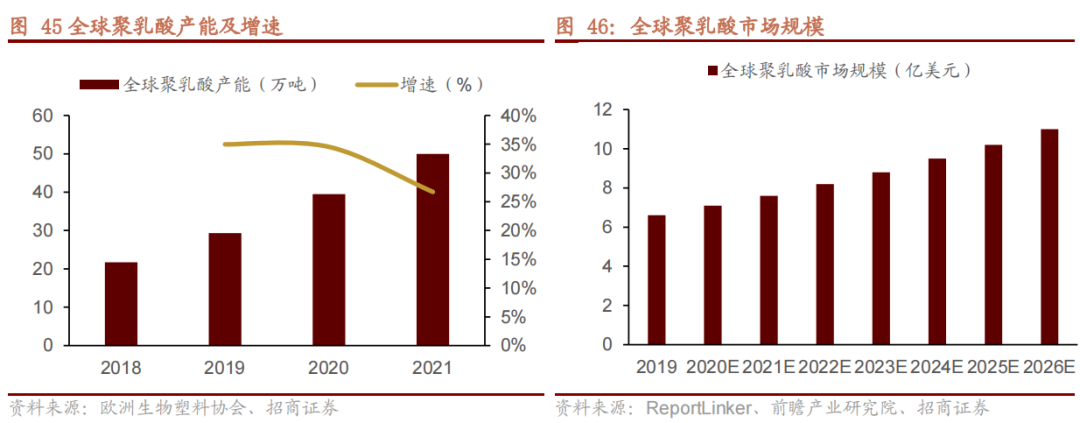
Benefiting from the era of green and environmental protection, the global production capacity of biodegradable plastics is steadily increasing, expected to reach 1.8 million tons per year by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.61% from 2018 to 2025. Among them, the growth of PLA production capacity is more rapid.
In addition, statistics from ReportLinker show that the global PLA market size had reached 660.8 million US dollars in 2019. Driven by its broad application prospects, the market will maintain a CAGR of 7.5% during the period of 2021–2026, with the global PLA market size projected to hit 1.1 billion US dollars by 2026.
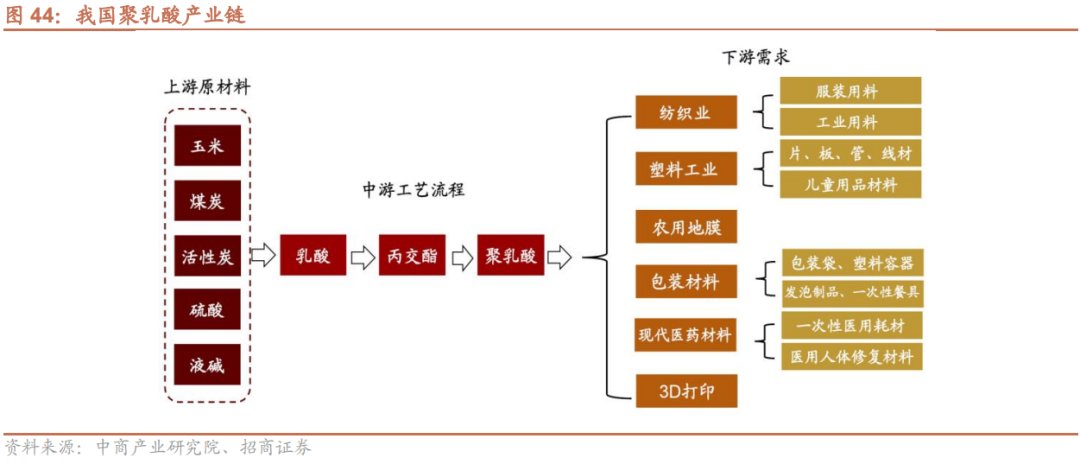
In the "Lactic Acid - Lactide - Polylactic Acid" Industrial Chain
The preparation of lactide, a key raw material, from lactic acid constitutes the core link, which mainly adopts two processes: ring-opening polymerization of lactide and direct polycondensation. The level of lactide synthesis and purification directly determines the performance of the final product, polylactic acid. Only high-purity lactide can be used to synthesize PLA with high molecular weight and excellent physical properties.
Domestic Substitution Status of Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Domestic enterprises are accelerating their rise with rapid production capacity growth. From 2020 to 2024, China’s PLA production capacity surged from 89,000 tons to 309,000 tons, and is projected to reach 365,000 tons in 2025. By constructing new production lines and expanding capacity plans, domestic players are gradually narrowing the gap with international counterparts.
In recent years, the market share of domestic enterprises has been on a steady rise. A growing number of small and medium-sized enterprises are also progressing steadily, leaving substantial room for further development.