Polylactic acid fully biodegradable film
Have you ever wondered where all the plastic mulch films used in farmlands end up each year?
They may be buried in the soil and remain undegraded for decades, and even enter the food chain, posing a threat to our health and the environment.
However, with the advancement of technology, a completely new type of environmentally friendly material - fully biodegradable plastic film - is quietly changing this situation.
Today, let's talk about this green technology and how it can bring about a "green revolution" in agriculture.
Why do we need biodegradable plastic films?
1.The "white pollution" problem caused by traditional plastic films
Traditional plastic film is difficult to decompose. Long-term use can lead to soil compaction, a decline in soil fertility, and even affect crop growth. According to statistics, China uses over one million tons of plastic film each year, a large amount of which remains in the soil, causing a serious "white pollution".
2. The environmental benefits of biodegradable film
- Complete degradation: After use, it can be decomposed by microorganisms and will not leave any harmful residues.
- Improving soil: Some of the film mulch can also release beneficial substances during the degradation process, thereby enhancing soil fertility.
- Reduce labor costs: No need for recycling, which saves manpower and time for clearing the plastic film.
Polylactic acid helps with degradable plastic films
Polylactic acid (PLA), also known as polypropylene glycol ester, due to its easy availability of raw materials, complete degradability, and non-harmfulness, has significant application significance in reducing environmental pollution, saving petroleum resources, and alleviating the greenhouse effect on the earth. Therefore, it is regarded as one of the most promising ideal green polymer materials with the best development prospects.
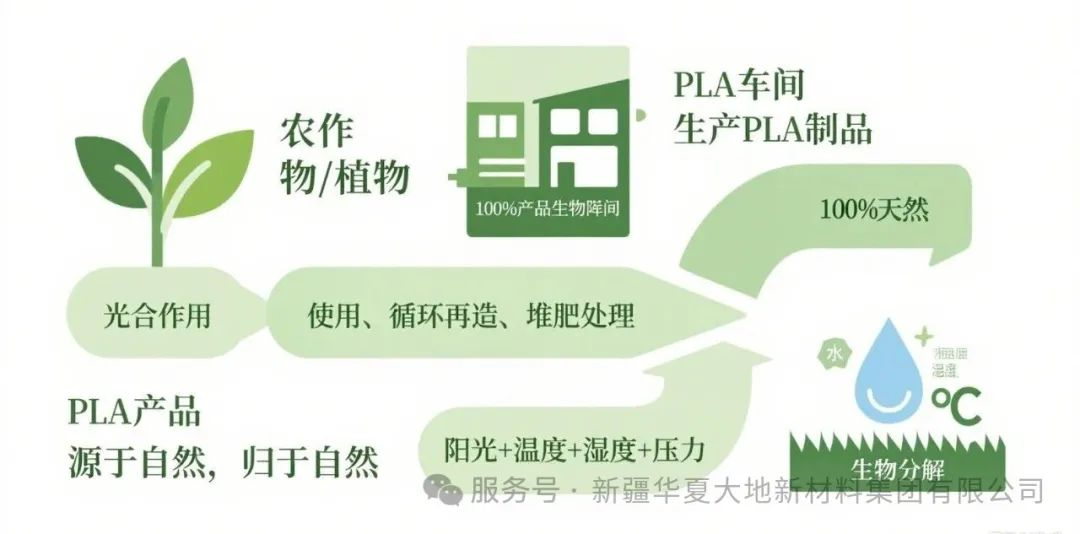
Corn, cassava, sorghum, etc. can all be used to produce polylactic acid (PLA). Among them, the conversion rate of corn to PLA can reach 70%. And China's corn production is around 150 million tons, so the raw material reserves are quite abundant. These crops can also be planted on a large scale artificially. In addition, straw, rice straw, and the roots, stems, and leaves of other crops or plants can also be used as raw materials. Moreover, kitchen waste or fish waste can also be obtained. And products made from PLA can be directly composted and buried in the soil. Under the action of natural microorganisms in nature, they can degrade and eventually completely break down into CO2 and H2O.

Polylactic acid has excellent mechanical properties, transparency, and gas and oxygen permeability. It can be directly processed and molded using general plastic equipment through extrusion, injection, stretching, spinning, and blow molding. It has good thermal stability, with a processing temperature range of 170 to 230 degrees Celsius. It has good solvent resistance. Products made from polylactic acid can be biodegraded and have good biocompatibility, glossiness, transparency, hand feel, and heat resistance. They also have certain antibacterial, flame retardant, and UV resistance properties. Therefore, it has a wide range of applications, such as being used as packaging materials, fibers, and nonwovens. Currently, it is mainly used in the fields of clothing (underwear, outerwear), industry (construction, agriculture, forestry, papermaking), and healthcare.
In terms of agricultural production, polylactic acid has excellent plasticity, heat resistance and physical processing properties. It can be processed into agricultural mulching films, which can compensate for the shortcomings of traditional mulching films, such as being fragile and non-biodegradable.
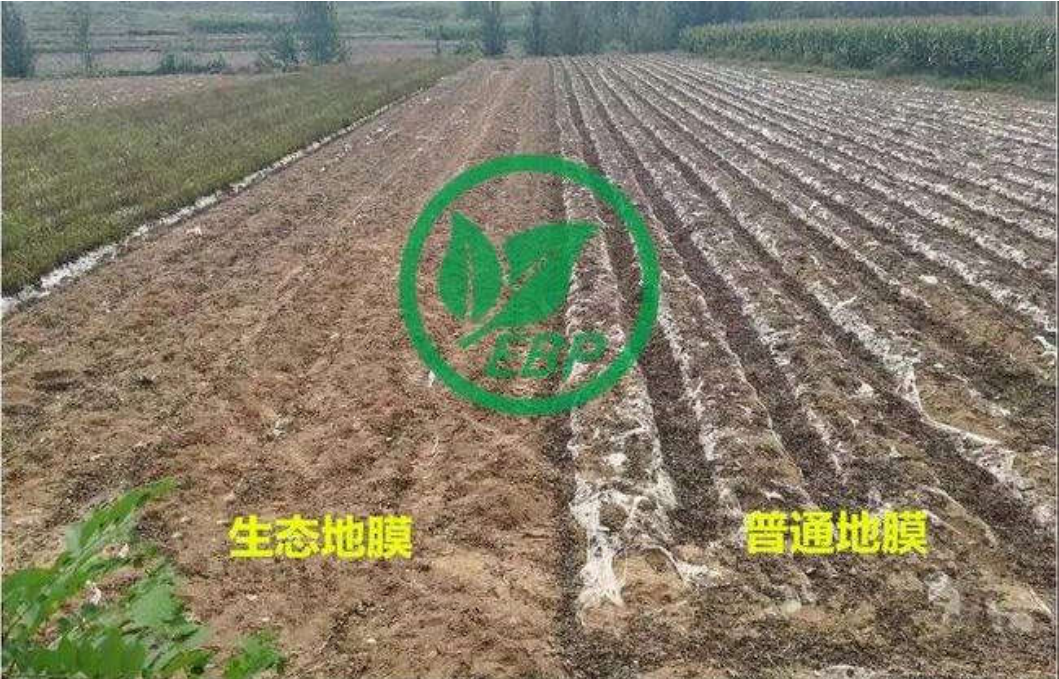

A comparative study was conducted on the degradability of ordinary polyethylene (PE) film and polylactic acid (PLA) film, as well as the growth of cotton under different film coverings. It was found that the PLA film began to degrade around 20 days, and the degradation area could reach about 80% by the cotton harvest time. Moreover, the PLA biodegradable film has comparable warming and moisture retention properties to the ordinary film, especially in terms of insulation performance, which is superior to traditional ordinary films. Additionally, the PLA biodegradable film can meet the normal growth needs of cotton. A comparative study was also conducted on the effects of ordinary polyethylene (PE) film and PLA film on watermelon cultivation. The experiment showed that the PLA film is degradable and does not cause environmental pollution. The comprehensive cost is comparable to that of ordinary PE, and covering the PLA film can promote the growth and development of watermelons.
With the increasing depletion of oil resources and the growing harm caused by traditional plastics to the environment through "white pollution", polylactic acid (PLA), characterized by "green and environmental protection", is enjoying excellent development opportunities. PLA film can not only address the pollution caused by agricultural films at the source and solve the "white pollution" problem in agriculture, but also provide a new opportunity for the management of agricultural solid waste. It is expected to replace ordinary films and be widely used in agricultural production, having a huge development space and application prospects in the agricultural production field.
The "Dual Carbon" Goal and the Outlook of Green Agriculture
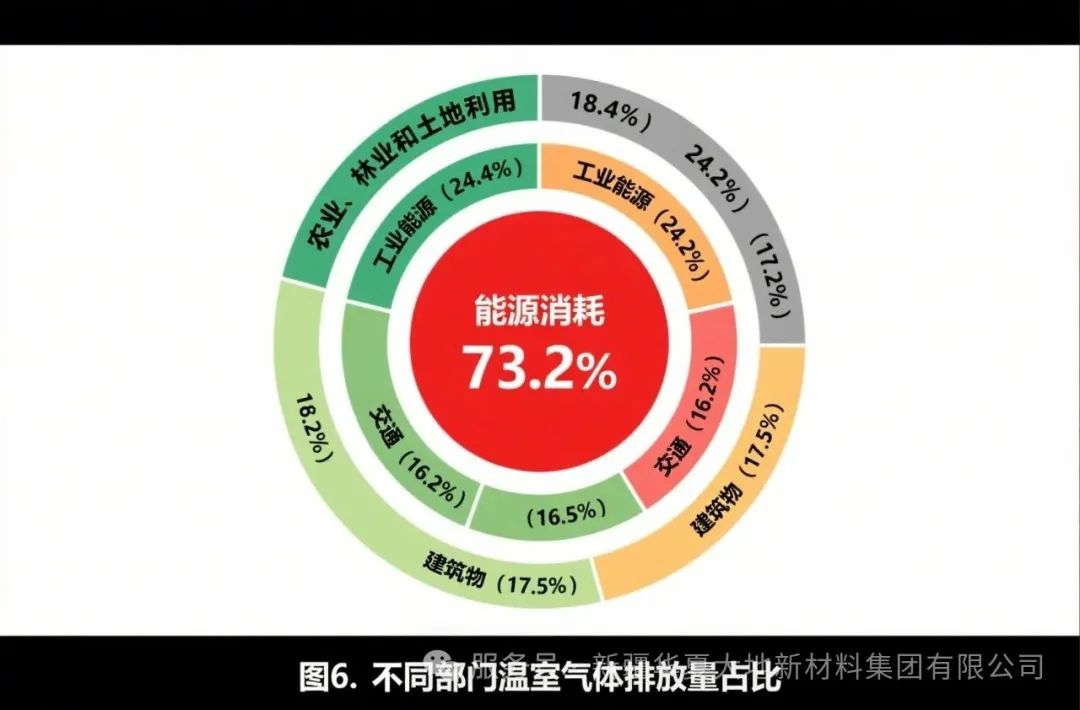
The "3060" targets for carbon peak and carbon neutrality have ushered in a new era of low-carbon development. According to statistics, emissions related to agriculture account for 18.4% of the total. Agriculture is one of the significant sources of greenhouse gas emissions and has great potential for carbon sequestration. Given the "dual identity" of agriculture, how to minimize agricultural carbon emissions and leverage its carbon sequestration function is a pressing practical issue for the development of agriculture in the new era. This promotes the green and low-carbon development of agriculture, which is an important means to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality.
Agriculture has a distinct green ecological background and plays a crucial role in the journey towards carbon peak and carbon neutrality. Paddy fields are artificial wetlands, vegetable gardens are artificial green spaces, and orchards are artificial forest lands. Compared with industry, agriculture inherently possesses "green" attributes and multiple functions. It is an important provider of ecological products and an important component of the ecosystem. Carbon neutrality is about harmonious coexistence between humans and nature and sustainable development. As a part of nature that has been tamed by humans early on, agriculture also needs to coexist with nature and contribute to carbon neutrality by reducing carbon emissions.
However, since agricultural films are closely related to modern farming, the "white pollution" accumulated over decades due to the extensive use of plastic films and their environmental impact has become a major obstacle hindering the development of green agriculture. In recent years, products such as photodegradable films and plastic films with added starch or straw have still been non-biodegradable products. After use, they disintegrate into plastic fragments or microplastic particles, posing greater potential pollution hazards. Therefore, biodegradable agricultural films based on polylactic acid are direct measures and effective means to replace traditional films and solve the problem of residual film pollution. Compared with traditional petrochemical products, the production energy consumption of polylactic acid is only 20%-50% of that of petrochemical products, and the carbon dioxide emissions are only 50%. They meet the requirements of sustainable development and are a completely natural and recyclable biodegradable material. With the proposal of the goals of carbon neutrality and carbon peak, and with the support of the plastic restriction policy, the application prospects of polylactic acid products in green agriculture are very broad.
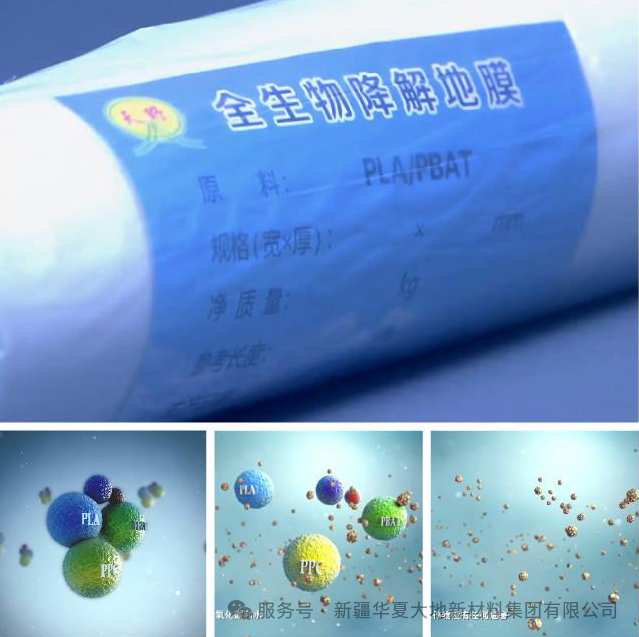
Project Introduction
The biodegradable plastic film produced in China is made from the globally recognized fully biodegradable materials PLA and PBAT, and all components are 100% safe and environmentally friendly materials. It is formed through the mutual blending and polymerization of multiple composite modification technologies. The product not only achieves the same mechanical strength, water retention and moisture retention functions as traditional PE plastic films, but also significantly promotes the growth of crop roots through appropriate degradation regulation and barrier treatment. From long-term usage observation, scientific experiments and a large number of user tracking data, it not only completely eliminates the problem of residual pollution from plastic films, but also has good degradation effect, high product cost performance and significant comprehensive benefits. It is the leading product in the field of biodegradable plastic films among its peers.
Based on the experimental and demonstration results of multiple plots and various types of crops in the northern region of China, the fully biodegradable plastic film produced by the company has fully adapted to the diverse environmental conditions in this area, such as short frost-free period, high ultraviolet intensity, seasonal droughts in certain periods, and numerous sandy slopes with windy climates. It has excellent environmental adaptability and significant yield enhancement effects. After use, with the assistance of microorganisms in the soil, the product will completely degrade into carbon dioxide and water before the next crop planting cycle (more than 180 days) arrives. Therefore, it has the functions of increasing agricultural production and income, eliminating the need for herbicides, avoiding the need for plastic film recycling, saving labor and field operation costs, etc.
Product features: The degradation time is adjusted according to the growth cycle of different plants. One area, one film; one item, one film. Generally, degradation begins 60-100 days after the film is laid, and the degradation accelerates in the later stage. Complete degradation is achieved 360 days later.
Product storage: Store in a dry, dark, and ventilated place. Do not store for a long term (<180 days).

Our biodegradable agricultural films actively comply with national policies, such as the following policies:
On December 22, 2023, the "Regulations of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region on Agricultural Plastic Film Management (Amended Draft)" was released. Article 13 of the draft states: The governments at or above the county level shall encourage production enterprises to carry out scientific and technological innovation, adopt new technologies and new materials to develop and produce fully biodegradable plastic films, encourage sales enterprises and users of agricultural plastic films to sell and use fully biodegradable plastic films, and gradually promote their use.
2. In order to strengthen the management of agricultural plastic films, prevent agricultural non-point source pollution, protect the agricultural ecological environment, and promote the green and high-quality development of agriculture, based on the actual situation of the autonomous region, the "Regulations on Agricultural Plastic Film Management in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region" has been formulated. It was revised and passed by the 9th meeting of the Standing Committee of the 14th People's Congress of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region on March 31, 2024, and will come into effect on May 1, 2024.


