Eighty thousand peace doves flapped their wings and eighty thousand balloons soared into the sky. This scene at the commemoration ceremony for the 80th anniversary of the victory of the Chinese People's War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression and the World Anti-Fascist War left a deep impression on many people. Many netizens were curious: Where did all those balloons go? Did they have any impact on the environment? We conducted interviews on this matter.
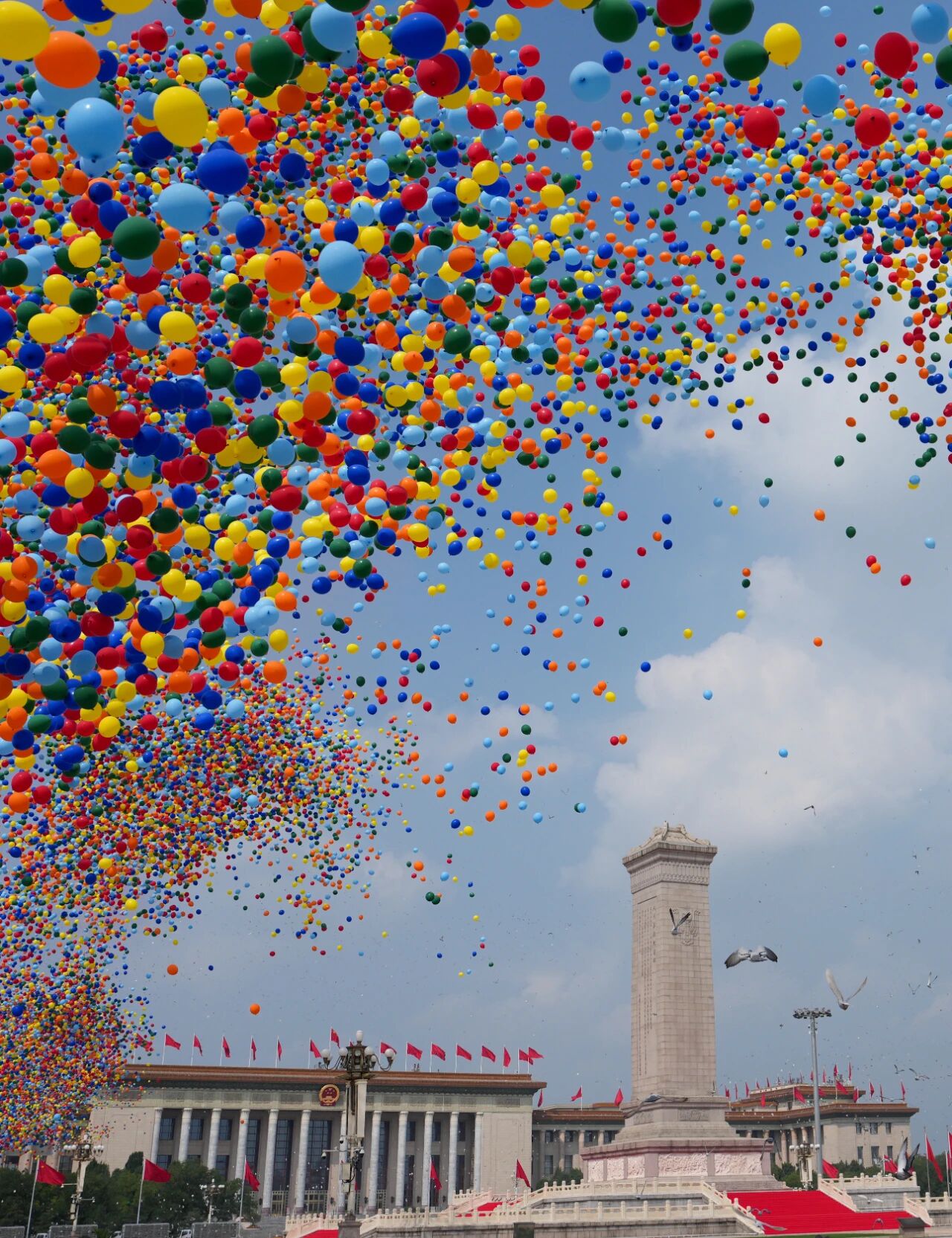 This was the scene of balloons and pigeons being released at the commemoration ceremony. (Photo by Mao Yu, Xinhua News Agency)
This was the scene of balloons and pigeons being released at the commemoration ceremony. (Photo by Mao Yu, Xinhua News Agency)
The 80,000 balloons released this time are significantly different from ordinary balloons. Dong Zhensheng, the general manager of Jiangsu Shijie Plastic Technology Co., Ltd., a manufacturer of windmill balloons, explained that the materials used for the balloons released during this event are significantly different from those of ordinary balloons in terms of composition and production process. Ordinary balloons are mostly made by mixing natural latex with various chemical additives, including vulcanizing agents, accelerators, and anti-aging agents. However, the balloons released at this conference are made of fully degradable natural materials, mainly consisting of natural latex, plant starch, and polylactic acid (PLA) fermented from plants such as corn and sugarcane. These materials are all biobased and degradable, with characteristics of being environmentally friendly, harmless, and fully degradable.
Don't underestimate the materials of these small balloons. "This special natural latex material is non-toxic, harmless, and non-irritating, and it also has the advantages of degradability and sustainability," said Dong Zhensheng. The raw materials and production processes used in the manufacture of these balloons have no precedent.
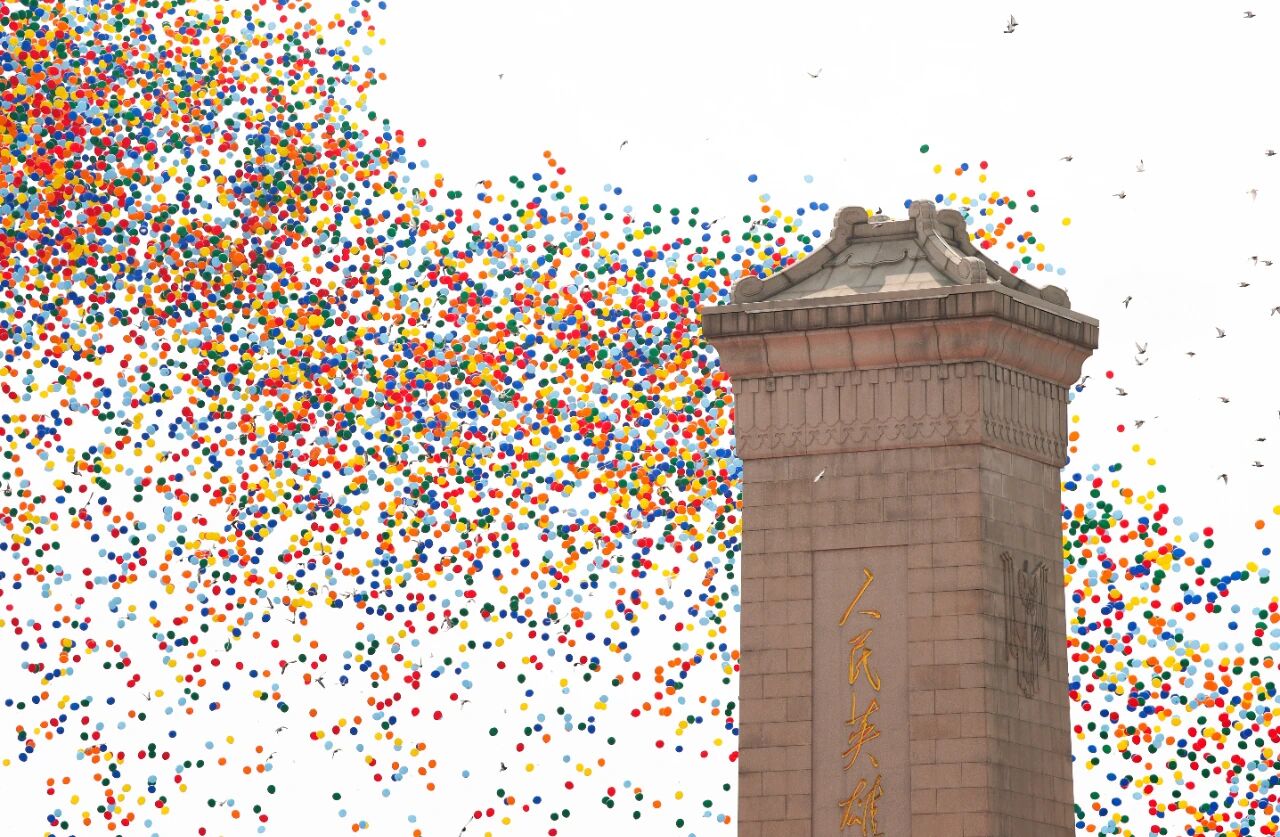 At the commemoration ceremony, pigeons and balloons were released. (Photo by Zhang Tao, Xinhua News Agency)
At the commemoration ceremony, pigeons and balloons were released. (Photo by Zhang Tao, Xinhua News Agency)
During the research and development process, a challenge emerged before the research team: How to adopt new biodegradable materials while maintaining the airtightness, tensile strength and elongation rate required for the balloons? "These performance requirements are in some way contradictory to the biodegradable nature of the materials," Dong Zhensheng said. The research team, through continuous experiments and technical breakthroughs, finally succeeded in achieving that the balloons possess excellent physical properties while having a high biodegradation rate, breaking through the key technical bottleneck of environmental-friendly materials in practical applications.
How high is the degradation rate of this type of balloon? The material used in this balloon will start to flake off on the surface after about one month under normal sunlight conditions. The natural degradation rate within 180 days can reach 60% - 70%. It can be completely degraded within one to one and a half years, and ultimately decomposes into water, carbon dioxide and organic matter, without causing permanent pollution.
Apart from corporate research, there are also some scientists dedicated to this field of study. Experts in the relevant field introduced that scientists are also researching a biogenic composite material that does not use aluminum foil and has a gas barrier property similar to natural latex.
Source: People's Daily (September 6, 2025, Page 06), Reporter: Dong Yingxue, Yao Xueqing, Original Title: "Where Did 80,000 Balloons Go (Fun Science Popularization)"
Editor: Hu Chengyuan, Chen Zihan