The recent market research report on "Bioplastic Packaging" published by the German consulting firm Ceresana conducted a survey of the global market for biobased and/or biodegradable plastic packaging materials.
The core conclusion is as follows: The increase in production capacity of polylactic acid (PLA), thermoplastic starch (TPS), and other biopolymers has improved the supply capacity and planning of products, driven down prices, and made these sustainable materials that replace fossil-based plastics economically attractive.
Nowadays, films, various containers, bottles and cups, sealing caps and bottle caps, as well as labels, tapes and filling packaging particles, are all manufactured using renewable raw materials. Market researchers predict that by 2034, the global sales of this sector will increase to approximately 32.1 billion US dollars.

The most important bioplastic in the packaging field: Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Not only is the production scale of bioplastics expanding, but their quality is also continuously improving. Heat-resistant varieties, customized barrier properties, and other innovative technologies are constantly expanding the potential application scope and usage scenarios of bioplastics. Polylactic acid (PLA) is usually extracted from plant starch and currently accounts for 30% of the bioplastics in the packaging market, making it the most important bioplastic in this field. The second is biobased but non-biodegradable plastic packaging, such as polyethylene (PE) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) made from sugarcane ethanol.
Ceresana predicts that the growth rates of polylactic acid (PLA) packaging and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) packaging will be the highest. Among them, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is produced through bacterial fermentation and is biodegradable. By 2034, the consumption of PLA and PHA bioplastics packaging is expected to increase by 10.3% and 7.2% respectively. The annual growth rates of biopolyethylene, biPET and biPA are expected to be only 5.3%.
One remaining challenge at present is that the price of bioplastics is often higher than that of traditional plastics made from petroleum or natural gas. Moreover, the reliance on intermediate products such as sugar and starch may pose risks and lead to significant price fluctuations.
The application of bioplastics in durable and high-performance products is increasing day by day.
According to a survey by Ceresana, bioplastics are increasingly being used to manufacture durable and high-performance products. However, at present, their main application field remains the short-term packaging for food and beverages. Among all bioplastics packaging, nearly 56% is used for packaging items such as bread, fruits and vegetables, water, soda and juice, dairy products, refrigerated and frozen foods, ready-to-eat meals and convenience foods, spreads, sauces and seasonings.
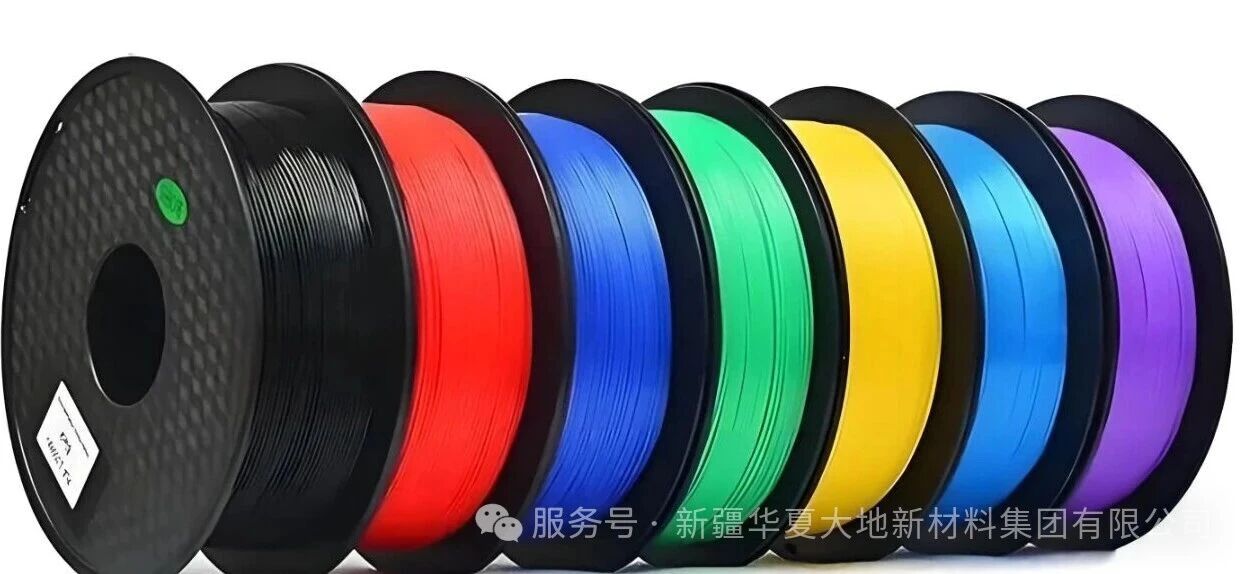
Just like traditional petrochemical plastics, these polymers made from biological raw materials each have their own applicable fields: for instance, biocompatibility is an important advantage for them in medical implant applications; while degradability is a necessary characteristic for products such as agricultural films and flower pots. In the 3D printing field, bioplastic filaments are also highly favored because they do not emit the smell of burnt plastic.
The trend towards eco-friendly packaging is not limited to Europe alone: According to a market research report by Ceresana, the world region with the largest consumption of bioplastic packaging at present is the Asia-Pacific region, accounting for approximately 42% of the global market.