Recently, the team led by Professor Qi Qingsheng from the National Key Laboratory of Microbial Modification Technology published a research result titled "Improving the Substrate Binding Pocket Flexibility of Leaf-Branch Compost Cutinase for Efficient and Complete Degradation of Commercial PBAT Plastic" in the online version of the international journal Chemical Engineering Journal. This study provides a brand-new highly active catalyst for the biodegradation and recycling of PBAT plastic waste. This research was jointly completed by Professor Qi Qingsheng and Associate Researcher Su Tianyuan from the National Key Laboratory of Microbial Modification Technology at Shandong University. Doctoral student Han Yuanfei from the laboratory was the first author of the paper. Shandong University is the first completion unit and corresponding author unit of this research.
 Polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT), as a biodegradable plastic, is a mainstream alternative to traditional non-biodegradable plastics, especially for agricultural film, replacing polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride. PBAT plastic has excellent ductility and thermal stability and has been widely used in the production of agricultural films, demonstrating significant advantages in biodegradability, which is of great significance for the sustainable development of agriculture. However, PBAT does not completely degrade in the natural environment, easily forming microplastics. Moreover, its degradation intermediates, terephthalic acid (TPA), have certain biological toxicity and accumulation in the environment will pose potential threats to the ecosystem. More importantly, the raw materials for synthesizing PBAT mainly come from non-renewable petrochemical resources. Large amounts of them being discarded into the environment will seriously exacerbate carbon emissions. To address these challenges, scholars at home and abroad have begun to actively research and design efficient PBAT degrading enzymes.
Polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT), as a biodegradable plastic, is a mainstream alternative to traditional non-biodegradable plastics, especially for agricultural film, replacing polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride. PBAT plastic has excellent ductility and thermal stability and has been widely used in the production of agricultural films, demonstrating significant advantages in biodegradability, which is of great significance for the sustainable development of agriculture. However, PBAT does not completely degrade in the natural environment, easily forming microplastics. Moreover, its degradation intermediates, terephthalic acid (TPA), have certain biological toxicity and accumulation in the environment will pose potential threats to the ecosystem. More importantly, the raw materials for synthesizing PBAT mainly come from non-renewable petrochemical resources. Large amounts of them being discarded into the environment will seriously exacerbate carbon emissions. To address these challenges, scholars at home and abroad have begun to actively research and design efficient PBAT degrading enzymes.
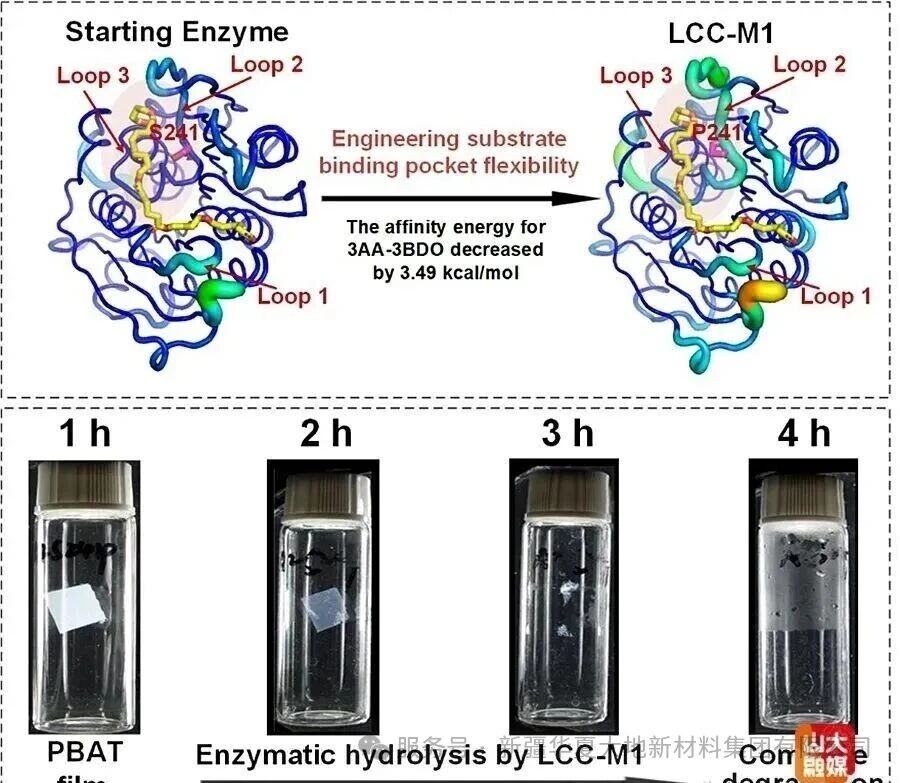
Engineering of the substrate-binding pocket enhances the PBAT degradation activity of plastic-degrading enzymes
The PBAT molecule contains two different ester bond structures, namely aliphatic and aromatic. Therefore, developing a plastic hydrolytic enzyme that can efficiently degrade both of these ester bond structures is the key to effectively recovering PBAT plastic waste. Previously, our team developed an efficient degrading enzyme LCC-A2 for PET plastic (ACS Catalysis, 2024), which could degrade over 90% of post-consumer PET plastic waste within 3.3 hours. In this study, by enhancing the flexibility of the key loop region of the substrate binding pocket of LCC-A2, and improving its adaptability to the PBAT substrate, a mutant LCC-M1 was obtained. This mutant shows excellent degradation ability for both PBAT ester bonds and can completely degrade the commercialized PBAT film without any pretreatment within 4 hours, completely degrade the commercialized PBAT/PLA blend plastic bag within 3 hours, and over 99% of the degradation products are the final degradation products. LCC-M1 is currently the most efficient PBAT degrading enzyme reported. The substrate binding pocket modification strategy developed in this study and the obtained PBAT degrading enzyme mutant are of great significance for solving the increasingly serious plastic pollution problem.
This research was supported by funds from the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Taishan Scholar Young Expert Program of Shandong Province, the SKLMT Frontier and Challenges Project, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province.







